The test system used in this review was an HP 8200 Elite. The computer came equipped with an Intel Core i5-2400 CPU, 4GB of DDR3 1333MHz memory, Seagate Barracuda 7200.12 ST3250312AS 250GB SATA 6 Gb/s hard drive, NVIDIA Quadro FX580 512MB PCIe graphics card and an Intel 82579-LM gigabit network card. For the operating system, I installed a fresh copy of Windows 7 Enterprise. I should also point out that our test system is not equipped with an mSATA port so we had to use an mSATA to SATA 6 Gb/s adapter card.
To test the performance of Samsung's 250GB 850 EVO M.2, I ran a series of benchmarks using CrystalDiskMark 3.0.1, HD Tach RW 3.0.4.0, ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46, AS SSD, HD Tune Pro 5.00, Anvil's Storage Utilities and Iometer. For comparison, I've also included test results from the Samsung 850 EVO mSATA, AMD Radeon R7, Silicon Power Slim S80, Samsung SSD 850 EVO, OCZ ARC 100, SanDisk Ultra II, Crucial MX100, SanDisk Extreme Pro, Samsung SSD 850 PRO, Plextor PX-256M6S, Toshiba Q Series Pro, Plextor PX-256M6M, Samsung SSD 840 EVO mSATA, OCZ Vector 150, OCZ Vertex 450, Silicon Power Slim S55, Samsung SSD 840 EVO, Seagate 600 SSD, SanDisk Extreme II, Plextor PX-256M5M, OCZ Vector, Plextor PX-256M5Pro Xtreme, Samsung SSD 840 Pro and Samsung SSD 840.
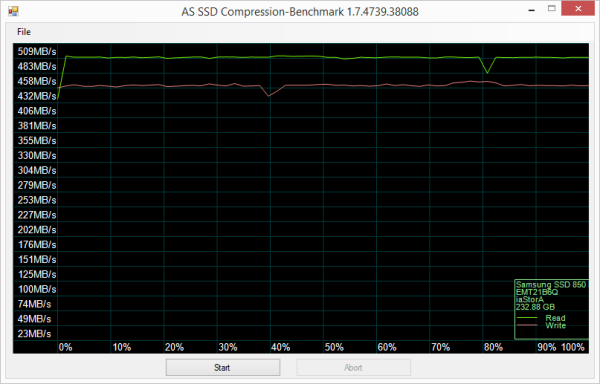
As I mentioned earlier, the 850 EVO M.2 is based on Samsung's MGX (S4LN062X01-Y030) controller chip. Looking at the screenshot above, you can see that it performs equally well with both incompressible (0%) and compressible (100%) data.
CrystalDiskMark 3.0.3:
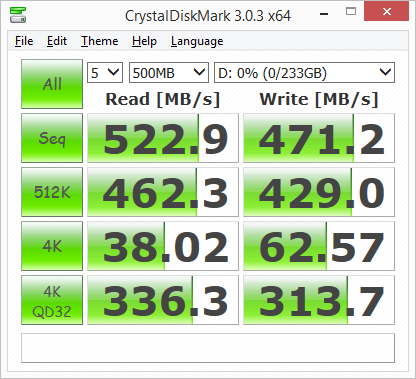
First, I ran a few quick tests using CrystalDiskMark. This benchmark tool measures the performance of a storage device by testing its sequential read and write speeds as well as its random read and write speeds using blocks 512K and 4K in size.
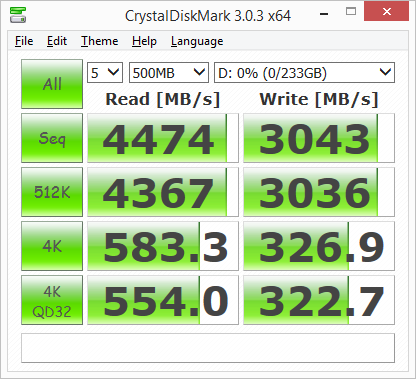
According to Samsung, the 250GB 850 EVO M.2 is capable of reading at 540 MB/s and writing at 500 MB/s. While the drive performed well, it came up a bit short of these numbers in CrystalDiskMark's sequential read and write speed tests. With RAPID mode enabled, these numbers increased considerably though. Looking at the screenshot above, you can see that the 850 EVO M.2 was able to read at 4,474 MB/s and write at 3,043 MB/s.
HD Tach RW 3.0.4.0:
Next, I used HD Tach to test the 850 EVO M.2's read, write and burst speeds as well as its seek times and CPU usage.

Samsung SSD 850 EVO M.2 250GB
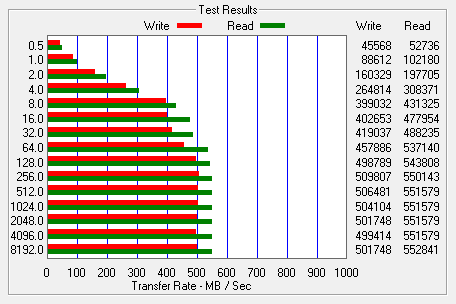
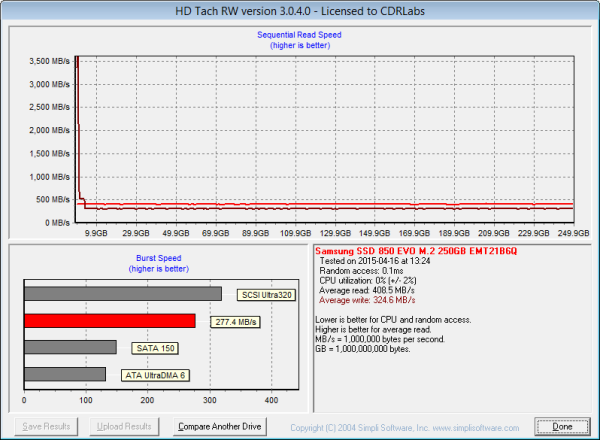
Looking at the screenshot above, you can see that the 850 EVO M.2 had average read and write speeds of 404.1 MB/s and 308.7 MB/s respectively, as well as a burst speed of 411.1 MB/s. The screenshot also shows the transition from TurboWrite to what Samsung calls "After TurboWrite" speeds. The 850 EVO M.2 starts writing at about 370 MB/s and then drops to about 300 MB/s when the consecutive write operation exceeds the size of the buffer.
Samsung SSD 850 EVO M.2 250GB (RAPID Mode)
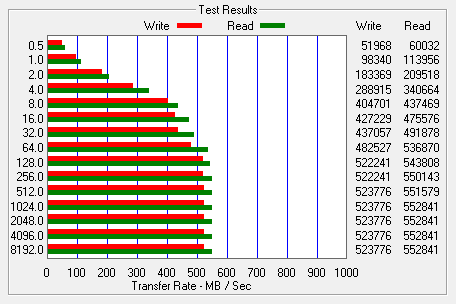
This time around, RAPID mode had very little effect on the 850 EVO M.2's performance. Most likely, this is due to the way HD Tach bypasses the file system when performing its read and write tests.
ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46:
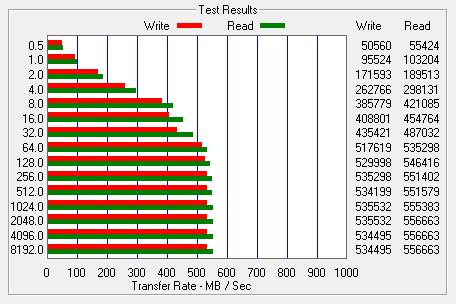
I also used ATTO Disk Benchmark to test the 850 EVO M.2's sequential read and write speeds. The tests are run using blocks ranging in size from 0.5KB to 8192KB and the total length set to 256MB.
When tested with ATTO, the 850 EVO M.2's read speeds topped out at about 552 MB/s and its write speeds at 509 MB/s. With RAPID mode enabled, the read and write speeds were all over the place, but for the most part, it was a considerable improvement.