The test system used in this review was an HP 8200 Elite. The computer came equipped with an Intel Core i5-2400 CPU, 4GB of DDR3 1333MHz memory, Seagate Barracuda 7200.12 ST3250312AS 250GB SATA 6 Gb/s hard drive, NVIDIA Quadro FX580 512MB PCIe graphics card and an Intel 82579-LM gigabit network card. For the operating system, I installed a fresh copy of Windows 7 Enterprise.
To test the performance of the OCZ Synapse Cache, I ran a series of benchmarks using CrystalDiskMark 3.0.1, ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46, Iometer, BootRacer and PCMark Vantage.
CrystalDiskMark 3.0.1:
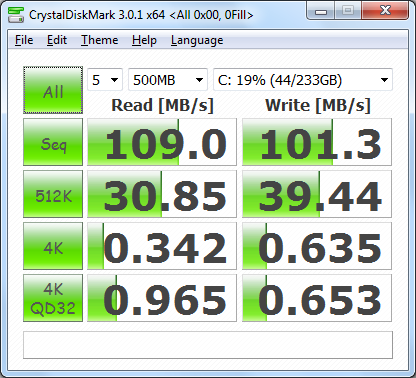
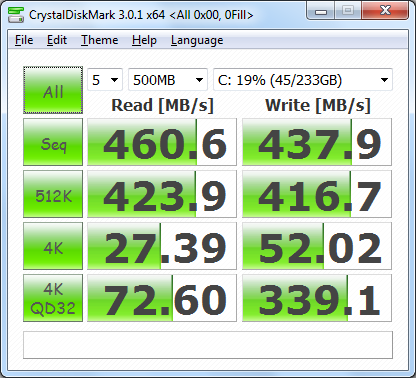
First, I ran a few quick tests using CrystalDiskMark. This benchmark tool measures the performance of a storage device by testing its sequential read and write speeds as well as its random read and write speeds using blocks 512K and 4K in size.
The performance improvement here is pretty impressive. By itself, the Seagate Barracuda 7200.12 was able to read and write at a little more than 100 MB/s. With the Synapse Cache enabled, these speeds increased by more than 336 MB/s. The 4K QD32 random write performance also jumped from a mere 0.653 MB/s up to an amazing 339.1 MB/s.
ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46:
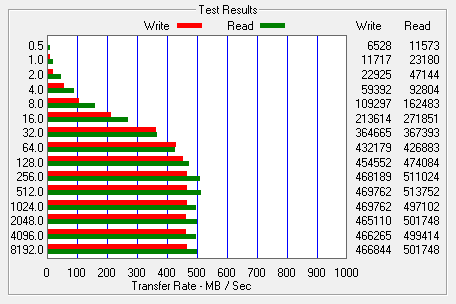
Next, I used ATTO Disk Benchmark to test the Synapse Cache's sequential read and write speeds. The tests are run using blocks ranging in size from 0.5KB to 8192KB and the total length set to 256MB.
The performance here is very similar to what we saw with CrystalDiskMark. With the Synapse Cache enabled, the read speeds topped out at 513 MB/s and the write speeds at nearly 470 MB/s.
Iometer:
I also ran a series of tests using Iometer. This tool can be configured to benchmark a number of things. In this case, I used it to measure the OCZ Synapse Cache's read and write speeds and the number of operations per second. The tests were run using both repeating and random bytes and a queue depth of 3.
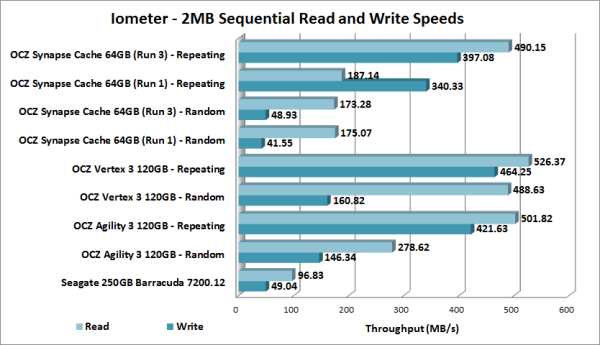
The Synapse Cache performed very well with compressible, repeating data. By the third run, our test system was able to read at 490.15 MB/s and write at 397.08 MB/s. Unfortunately, the Synapse Cache did not perform nearly as well with randomly generated data. After the third run, the read speed topped out at only 173 MB/s and its write speed was actually slower than what we saw with the hard drive alone.

The Synapse Cache also gave our test system a considerable performance boost when doing random reads and writes. By the third run, it was able to read at 41.02 MB/s and write at 184.68 MB/s with repeating data. The Synapse Cache did not perform quite as well with randomly generated data. However, its speeds were still better than the Seagate Barracuda 7200.12 by itself.

According to OCZ, the Synapse Cache is capable of 10,000 IOPS when reading and 75,000 IOPS when writing 4K blocks. By the third run, it reached 10,500 IOPS when doing a random read and 47,277 IOPS when doing a random write with repeating data.