The test system used in this review was an HP 8300 Elite. The computer came equipped with an Intel Core i5-3470 Ivy Bridge CPU, 16GB of DDR3 1600MHz memory, Seagate Barracuda ST250DM000 250GB SATA 6 Gb/s hard drive, NVIDIA Quadro FX600 1GB PCIe graphics card and an Intel 82579-LM gigabit network card. For the operating system, I installed a fresh copy of Windows 7 Enterprise.
To test the performance of the two Plextor PX-256M5P drives in RAID, I ran a series of benchmarks using CrystalDiskMark 3.0.1, ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46, AS SSD, Anvil's Storage Utilities and Iometer.
For simplicity's sake, I used the RAID controller built into the Intel Q77 Express chipset. I also installed the latest version (11.6.0.1030) of Intel's Rapid Storage Technology driver and used the included utility to configure the RAID array.
CrystalDiskMark 3.0.1:
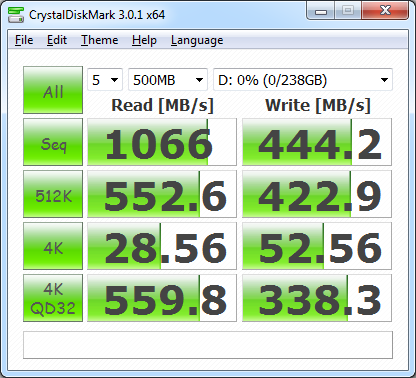
First, I ran a few quick tests using CrystalDiskMark. This benchmark tool measures the performance of a storage device by testing its sequential read and write speeds as well as its random read and write speeds using blocks 512K and 4K in size.
The two PX-256M5P's performed very well when configured in a RAID 0 array. The drives were able to read at 994.9 MB/s and write at a blistering 825.4 MB/s. The sequential read speed jumped to 1066 MB/s when using RAID 1. However, its write speed dropped to 444.2 MB/s which is on par with what we saw in our original review when testing a single PX-256M5P.
ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46:
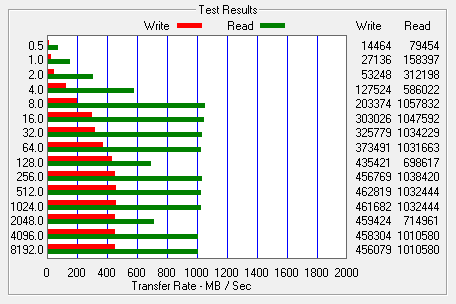
I also used ATTO Disk Benchmark to test the PX-256M5P's sequential read and write speeds. The tests are run using blocks ranging in size from 0.5KB to 8192KB and the total length set to 256MB.
When configured as a RAID 0 array, the two PX-256M5P's were able to read at 1,061 MB/s and write at 916 MB/s. The read speed was also quite good in RAID 1. However, the write speed topped out at only 462 MB/s.
AS SSD:
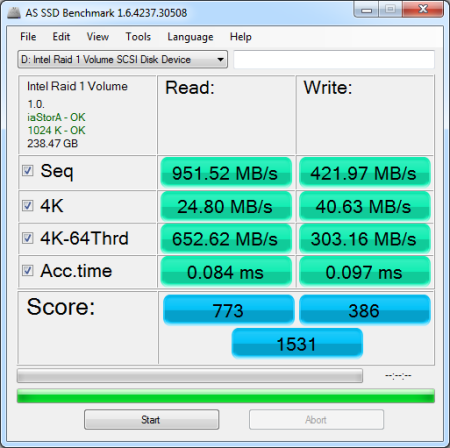
AS SSD is a relatively new benchmark designed specifically for solid state drives. The application contains five synthetic tests used to determine the sequential and random read and write performance of a drive.